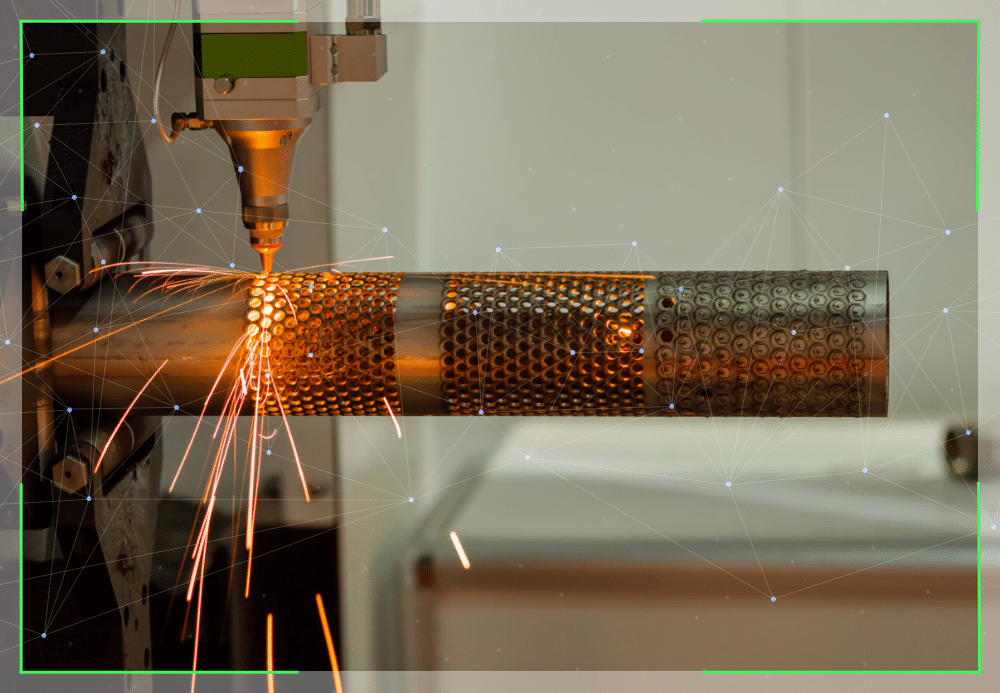
As with most tools and equipment that perform complex, often arduous tasks, maintenance is essential to keep them in optimum working condition. Tube lasering units are no exception, and depending on the type of unit in question, maintenance can be the difference between continued flawless operation and a host of time-consuming, expensive problems. This blog will first examine the two main types of tube laser cutters and then describe the maintenance regimes and best practices that should be employed to keep them in peak working condition.
Fibre lasers
Fibre laser cutting machines use a bank of diodes to produce light. This light intensifies as it passes through fibre optic cables, amplifying the photons. The result is a highly efficient laser beam with some of the following features:
Advantages
- No moving parts or mirrors—Nothing must be aligned for a fibre laser to operate.
- Low maintenance requirements—The maintenance required to run fibre lasers consistently is almost nil, making them highly cost-effective and straightforward.
- Superior electrical efficiency—Running costs are lower.
- Environmentally friendly—Less power means lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Speed—Fibre lasers can cut thin materials almost three times faster than CO2 units.
- Reflective materials—Copper, brass, and aluminium can be cut using fibre lasers.
Disadvantages
- Issues cutting thicker materials—Once the metal’s thickness passes around 5mm, the cutting speed is drastically reduced, and the resulting cuts may not be as clean as required.
Maintaining fibre laser cutters
As long as the unit receives clean, chilled water and the air filters are replaced routinely, a fibre laser cutter is virtually free from preventive maintenance requirements.
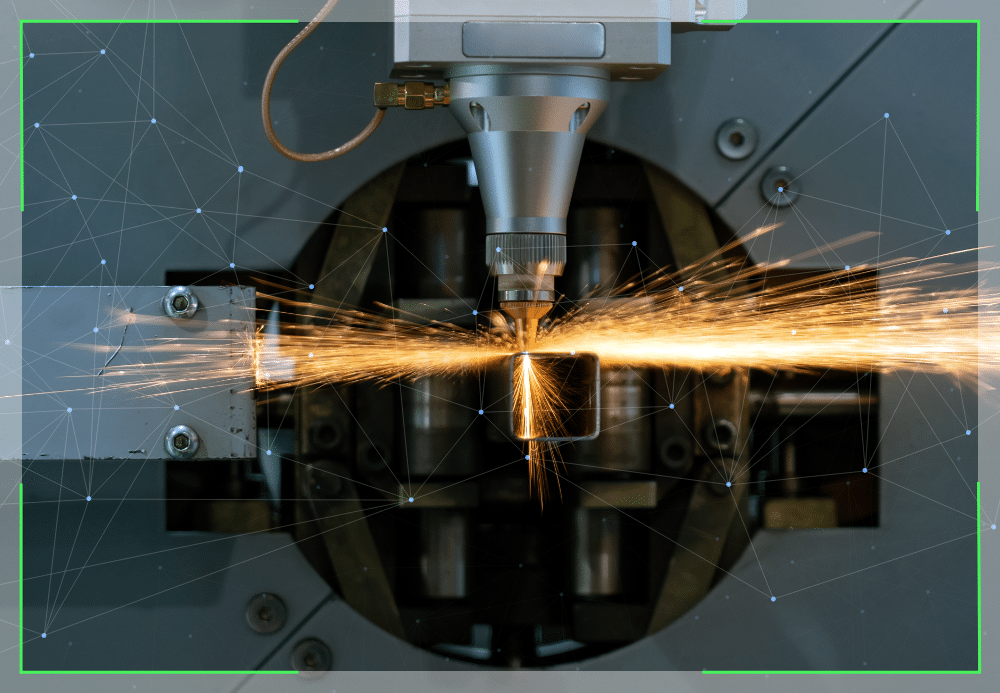
CO2 lasers
CO2 laser cutting machines use agitated CO2 molecules to release photons, which can then be focused into a beam. This is achieved using a combination of optical mirrors and lenses.
Advantages
- Superior cutting abilities on thicker materials—Cutting is faster and more effective than fibre lasers.
- Smoother cut edges—Again, this is especially true of thicker materials, but CO2 lasers typically leave a smoother finish when the cut is completed.
Disadvantages
- Extreme sensitivity—If the machine is nudged or vibrated too vigorously, the focusing mirrors will almost certainly require realignment. A specialist must perform this, and it is expensive and time-consuming.
- Elevated maintenance costs—CO2 lasers are much higher-maintenance machines, contributing to elevated running costs.
- High power consumption—If a CO2 laser is used with any frequency, the electricity bills will skyrocket, as they draw a lot of power to run.
- Inability to cut reflective materials—if the laser is reflected into the machine, it can be damaged beyond repair very quickly.
Maintaining CO2 laser cutters
The situation with CO2 lasers could not be more different. The fumes, smoke, and debris that the intense process can create (depending on the materials being cut) build up within the machine and components like the chiller and filters. This can lead to issues like overheating and system failure, so they require specific maintenance actions, namely:
Extractor fan
- Check for any accumulation of dust and debris on the impeller.
- Disconnect the unit from the electrical supply.
- Remove the extraction hoses.
- Clean the fan and ducting through the inlet and exhaust ports.
- Use a soft brush and avoid damaging any sensitive elements.
Air compressor
- Check for the normal function of the compressor and any obstructions in any filtration elements.
- Inspect the delivery hose (compressor to cutting head), ensuring there are no obstructions and enough air is reaching the nozzle. This is especially important, as reduced airflow can lead to flames when cutting specific materials.
Runners and linear guide
- Regularly lubricate the runners and the mechanism that allows the bed to be raised and lowered using light oil. This reduces wear on moving components and facilitates cutting speed.
Laser optics
- Monitor your cutting results and note any reduction in their quality, which may be due to dirty optics that reduce the strength of the beam.
- Clean your lens and mirror carefully using an IPA solution or acetone on cotton buds. If necessary, do this after around 10 hours of operation (the nature of the materials being cut dramatically affects this). Dirt that gets scorched onto your optics can permanently damage them and force their replacement, which is expensive.
Chiller unit
Water chillers help to regulate the heat produced by laser cutters and must be monitored carefully.
- Remove any build-up of material from the filters regularly.
- Check for water contamination.
- Replace with de-ionised or distilled water.
Bearings
Laser cutting machines use a lot of bearings to facilitate smooth cutting and engraving.
- Inspect them regularly and perform any cleaning and lubrication as required.
Elastic belt drive
Tube laser cutters use several timing belts in the drive system that must be accurately tensioned.
- Use the tensioning screws until the manufacturer’s recommended specifications are matched.
Contact us
To discuss maintenance and other aspects of tube lasers, please contact the Bend-Tech Group today. Our team of dedicated professionals will gladly provide all the advice, guidance, and information you require.





About The Author: Highjumpdev
More posts by Highjumpdev